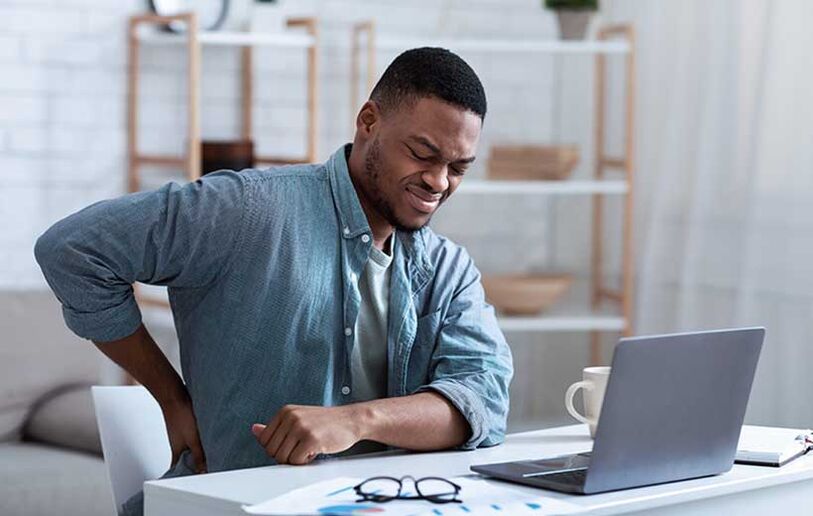
Osteochondrosis is a common degenerative-dystrophic lesion that affects the intervertebral disc, adjacent vertebrae and nearby ligaments.
The disease does not develop immediately, develops over many years, while the onset can occur at a relatively young age (18-20 years), and has several stages:
- Stage I - "cracks" in the fibrous ring and intradiscal movement of the nucleus pulposus, but there are no radiological signs yet;
- Stage II - the nucleus pulposus continues to degenerate, the height of the disc decreases, the fibrous ring "dry", the affected intervertebral joint becomes unstable, and to compensate, the back muscles are in constant tension, causing pain and "overwork", signsosteochondrosis visible on x-ray;
- Stage III - the disc ruptures, the nucleus pulposus prolapses forming a hernia, the stage is characterized by many neurological symptoms, inflammation, and edema;
- Stage IV - adjacent elements of the joint are involved in the lesion.
Osteochondrosis of the spine can also occur in different parts of the spine and, depending on this, have different names:
- cervical - most often localized between the fifth and seventh cervical vertebrae (the most mobile joint);
- chest - a variant indicated by pain, which can be confused with diseases of other organs of the chest;
- lumbar - the most common type due to the greatest mobility of this part and the load placed on it;
- common - involves several parts (for example, cervicothoracic).
Reasons for the development of osteochondrosis
There is no single comprehensive theory that fully explains the cause of this disease. It is multifactorial, therefore, a tendency is necessary as a trigger, and for its manifestation - a complex of internal and external stimuli.
Exogenous risk factors:
- excessive stress, physical labor, occupational hazards (moving heavy objects) are common causes of osteochondrosis in men;
- spinal cord injury;
- sharp and uneven jerks, body bending, twisting;
- sedentary work, physical inactivity;
- constant repetitive movements (carrying a bag on the same shoulder, tilting your head to your ear when talking on the phone);
- climatic conditions.
Endogenous risk factors:
- male gender (osteochondrosis occurs less often in women);
- overweight and high;
- abnormalities of the development of the musculoskeletal system, weakness of the back muscles;
- poor posture;
- foot diseases (arthrosis, flat feet);
- violation of intervertebral joint trophism;
- pathology of internal organs.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Typical signs of this disease: pain in the spine and muscles at rest, limitation in movement, "fatigue" of the affected area. The patient tries to either "unload" by leaning on a chair, leaning on his hands, trying not to stand on his feet for a long time, or by rubbing and kneading them, relieving muscle tension. Depending on the location, the pain may be slightly different, and new, more specific symptoms are added.
With cervical osteochondrosis, unpleasant sensations will occur in the occipital region or the neck itself, intensifying when tilting or turning the head. Because of pinching the nerve roots, tingling or burning may appear in the fingers and palms, and with more serious damage, restrictions in their movement.
But the main danger of this case is that near the spine in this area there is an important artery that supplies blood to the brain. Gradually they become pinched, so this type of osteochondrosis is characterized by dizziness and "spots" in front of the eyes due to insufficient nutrition of the main organs in the body.
Among all types of osteochondrosis, damage to the thoracic region is less common than others and difficult to diagnose. Pain in this area is similar to pain in the heart, lungs, esophagus or neuralgia. Therefore, patients first of all turn to cardiologists, gastroenterologists or pulmonologists, long avoiding the doctors of the specialization they need, until all other pathologies are excluded, or thoracic osteochondrosis is suspected. The discomfort is localized between the shoulder blades, worsens when bending over, you may experience a lump in the throat or difficulty breathing, and numbness in the chest.
The most common and most typical type is lumbar osteochondrosis. The symptoms are most often associated with this disease: pain in the area with the same name, which increases when turning, bending, or standing for a long time, and can radiate to one or both legs.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
The doctor begins by collecting complaints and anamnesis (family, life and disease), which analyzes the presence of predispositions, external and internal risk factors, the relationship of symptoms and the development of lesions.
The inspection consists of:
- neuro-orthopedic, where the static and dynamic function of the spine is evaluated (posture, presence of scoliosis, muscle tone and various movements of intervertebral joints and limbs);
- neurological - determination of reflexes and compression vertebrogenic syndrome, motor and sensory functions, quality of tissue trophism.
The simplest and most accessible instrumental diagnostic methods for osteochondrosis of any part of the spine (cervical, thoracic or lumbar) are non-contrast and contrast (discography, venospondylography) X-ray studies that reveal the narrowing of the intervertebral disc, the degree of herniation. prominence, and the condition of blood vessels. A little less often, more informative magnetic resonance imaging is used, with which you can accurately assess the degree of damage to the intervertebral disc, the size of the hernia, the presence of compression of the spinal cord, roots, and surrounding tissues. If MRI is contraindicated, it is replaced by computed tomography, which determines the condition of the vertebra itself, spinal canal, and ligament calcification.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
First of all, it is necessary to reduce as much as possible the risk factors, which the doctor found during the survey. Eliminate axial loads, limit the severity of objects carried, sometimes change traumatic jobs related to physical labor, reduce weight if you are overweight, include a minimum of sports in your daily schedule if you are not physically active. This will only help to slightly reduce the level of pain due to osteochondrosis and the risk of complications, although it will not slow down its development.
Treatment must be comprehensive and combine not only drug methods, but also various types of effects on the vertebral muscles and the spine itself. You can't just take pills for osteochondrosis on your own and hope to get better; any procedure and medication can only be prescribed by a neurologist. The specialist bases his recommendations on each specific case and the individual characteristics of the patient, so that the treatment does not cause more suffering than the disease itself.
For osteochondrosis, exercise therapy is indicated, which is first carried out in a special hospital room so that the doctor is sure that the patient is doing the indicated exercises correctly. The different localization of lesions implies different complexes aimed at maintaining the back muscles, increasing blood circulation and trophism of the intervertebral discs and the vertebrae themselves, and reducing their friction.
Therapeutic massage also has a good effect on the course of the disease in osteochondrosis; physiotherapy, manual therapy, acupuncture, osteopathy, and spinal hardware traction are performed with care. The course of treatment and its methods are determined by the doctor based on the level of development of the lesion, the manifestation of pain and the individual characteristics of each specific case.
Prevention of osteochondrosis
If you take timely measures to prevent the development of the disease, then the treatment may not be necessary. This should also be approached holistically: reduce the risk factors listed in advance (even before discomfort appears), try to distribute the load evenly, monitor posture from childhood, receive adequate nutrition with all the necessary vitamins, and regularly engage in sportswhich supports (for example, swimming).
To prevent the development of osteochondrosis, gymnastics plays an important role: there are special exercises that reduce the load on the spine. You can consult an orthopedist or a neurologist about them.
But regular morning exercise will help maintain muscle tone, relieve spasms and improve blood circulation so that interarticular disc trophism is not disturbed. To prevent the development of physical inactivity in sedentary work, it is necessary to warm up regularly and perform exercises indicated for the prevention of osteochondrosis.